Sensorfy enables predictive maintenance by making industrial assets and machines smart. With their IoT predictive maintenance platform, the company enables real-time monitoring of industrial assets and machines to reduce machine downtime, lower maintenance costs and increase throughput. With smart sensors, Sensorfy can detect machine failures before they happen and monitor machine performance in real-time.
At the core of everything, at Sensorfy, innovation and sustainability are the main drivers. Together as a team, the company strives to create a more suitable world by lengthening the lifetime of assets and machines using smart sensors and predictive maintenance.
Predictive maintenance offers Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) new revenue streams by offering intelligent solutions through smart IoT sensors which collect real-time data. This creates a great opportunity to improve operational efficiency by reducing the number of equipment failures, and unplanned maintenance and reducing maintenance costs.
Interview with Gijs Meuleman, CEO at Sensorfy.
Easy Engineering: What are the main areas of activity of the company?
Gijs Meuleman: We’ve worked with several industrial manufacturers to design scalable custom-made Industrial IoT solutions to monitor their assets in real-time. Our technical knowledge makes the difference. We’ve built an IoT predictive maintenance platform that ensures the highest industrial IoT standards. We integrate smart wireless sensors and advanced analytics to enable predictive maintenance to monitor industrial assets in real-time.
We focus on 3 main markets including:
- Railway infrastructure
- Access building assets including automatic doors, elevators and escalators
- Industrial equipment
We work toegther with our clients in their product innovation and support them throughout the whole process from concept, engineering, industrialization and predictive maintenance.

Conpect:
- Business and feasibility scan
- Asset failure mode analysis
- Use cases
- Solution requirements
- System architecture
- Proof of concept
Engineering:
- Electrical engineering
- Mechanical engineering
- Embedded software development
- Algorithm modeling and design
- Prototype
- Data analytics
- Field testing, validation, and qualification
Industrialization:
- Tooling
- Certification
- Testing
- 0-series
- Solution production and ramp-up
Predictive maintenance:
- Real-time deployment
- Platform integration and dashboarding
- Integration into running your business
- Predictive analytics
- Actionable insights to optimize your assets

E.E: What are the ranges of products?
G.M: We’ve built an IoT predictive maintenance platform that ensures the highest industrial IoT standards. We integrate smart wireless sensors and advanced analytics to enable predictive maintenance to monitor industrial assets in real-time.
Our IoT Predictive Maintenance Platform is comprissed of 3 main products that are customized based on our client’s needs. These 3 include
Sensor Hub which includes:
- Smart sensor(s)
- Smart gateway
- Connectivity
Nexus Hub which includes:
- Device management
- Cloud data storage
- API integration
Insight Hub:
- Algorithm development
- Data visualization & dashboarding
- Predictive maintenance insights
E.E: What’s the news about new products?
G.M: We are now developing a new version of or nexus platform which will provide additional flexibility and options to our customers. We’re expecting to launch the new version by the end of 2022.

E.E: At what stage is the market where you are currently active?
G.M: We see that OEM’s are slowly transitioning into digitalization and predictive maintenance but there is a high interest in it. Most people are aware of the benefits of predictive maintenance but the implementation is still quite complex and takes a lot of time and planning. Still for many companies predictive maintenance remains a concept, but pressure to optimize efficiency means manufacturers can’t afford to delay the transformation.
Whether it is an OEM or a plant owner, making the transition to predictive maintenance – though it seems worth it – can seem overwhelming at first. While the benefits of preventative maintenance speak for themselves, it may seem daunting to get started. With unplanned downtime costing industrial manufacturers an estimated $50 billion each year, finding a way to optimize the process is business critical.
Predictive maintenance is less about technology and more about change management. Customers need to see this as an opportunity to change their operating models, which can deliver higher uptimes and reduce the cost of maintenance drastically. Making the transition from a preventive or reactive maintenance strategy to a predictive approach is not an easy undertaking. Predictive maintenance requires technological and process innovations to continuously gather sensor data from a physical asset and use advanced analytics for additional insights. A successful transformation is only possible when an organization prepares for it properly and innovates their whole processes and products.
We see there are the common challenges in implementing predictive maintenance.
The main challenges include:
- It’s a big investment
- Current assets are not compatible with smart sensors
- Integration with an operational Business Intelligence System
- Traning for employees is needed who will work with the new technology
- New skill set might be needed – hire specialized personnel to control the predictive maintenance program
- Privacy and security concerns
- Change management – Maintenance and/or factory staff is reluctant to change

E.E: What can you tell us about market trends?
G.M: The main trends within our industry include
Digitalization and servitization
Digitalization enables companies to innovate their business models and offer additional services. A highly topical example is servitization, the shift toward a model that is not based on revenue from the one-off sales of products or assets, but on recurring revenue from services related to those products/assets. You could think of making these available to the client for their operation or taking care of their maintenance on the basis of a service-level agreement. In the ultimate form of servitization, the complete product or asset is offered as a service; we designate it as X-as-a-Service, where X stands for the product/asset concerned.
Due to the increasing complexity of the technology and business, asset owners/operators are increasingly focusing on their core business. They organize their operation to be ‘lean & mean’, outsourcing supporting services and therefore divesting, for example, their technical service department. For service & maintenance of their assets, they rely on external parties. These can be dedicated service providers, but the OEMs which supplied the assets are natural partners of choice, because of their equipment expertise and their comprehensive offer of original parts. For an OEM, this means that the focus of its business model shifts from product to service. As a consequence, the relationship between the OEM and the asset owner is no longer limited to the one-off purchase of an asset, but increasingly covers the entire lifecycle of the asset. Instead of a business model based only on product sales, the OEM will have to adopt a lifecycle business model including the delivery of services such as maintenance.
To support OEMs and companies in this transition we wrote an Ebook: How to 3x your company valuation focusing on the different business models available and how to make the transition towards servitization.
Industrial IoT
In the asset business, digitalization implementations often take the form of an Internet of Things (IoT) solution. It starts with making an asset “smart” by providing it with smart sensors (which have a processing unit and a communication interface integrated) and connecting them to an IoT network. The sensors take measurements and the collected data is pre-processed before it is sent to the cloud for storage and further processing; the resulting data is analyzed to derive relevant operational information, if need be, with the aid of AI algorithms

Computing power and AI
We see computing power steadily increasing over the years, due to the ongoing miniaturization of semiconductors (following the famous Moore’s Law). This has facilitated the trend toward big data, i.e. collecting, storing, and analyzing massive amounts of data for the sake of monitoring and control. More and more, AI (artificial intelligence) is used in advanced data analytics for detecting trends and correlations in big data sets that conventional algorithms cannot uncover.
The rise of predictive maintenance
Interest in predictive maintenance for machine operators is growing rapidly in the industry, thanks to advancing digitalization, the rise of Industrial Internet of Things IoT, and – last but not least – the rapid development of artificial intelligence AI and machine learning including deep learning.
To the original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) that have supplied the assets, the predictive maintenance business case is less clear. In some cases, OEMs do not yet provide any service and maintenance, and if they do, they often still have a transactional business model. This conventional business model is based on revenue from incidental corrective maintenance, including the delivery of original spare parts. The aim of predictive maintenance is to eliminate this relatively expensive corrective maintenance as much as possible, and to replace it with cheaper interventions that can be planned more efficiently on the basis of predictions.
When it comes to critical assets, it important to detect failures before they happen by leveraging data to make accurate predictions. With the rise of AI in predictive maintenance, industrial companies are being triggered to reevaluate software solutions. Businesses are now keener on learning how collect data and use it to make accurate predictions about assets health and condition. Predictive maintenance is a key area that can lead to time and cost savings
To support OEMs and companies with the implementation of predictive maintenance we wrote an Ebook: Predictive Maintenance from Scratch
A more sustainable industrial industry
A study by PWC shows that 9 out of 10 industrial companies believe digitization offers their companies more opportunities than risks. Still many organizations keep struggling to implement digital change. The rise in investments in predictive maintenance as a result of IoT adoption, as well as the need to prolong the lifetime of ageing industrial machinery, are all driving the predictive maintenance market forward. The sustainability of industrial operations is also playing a crucial role in industrial companies. We see an increase in the need to gain insights into the performance of industrial machinery to prolong the lifetime of ageing industrial machinery. As a result, we see a spike in the interest in predictive maintenance.

Unplanned downtime is one of the biggest unforeseen costs for industrials. According to Forbes overall, unplanned downtime costs industrial manufacturers as much as $50 billion a year. And the average manufacturer confronts 800 hours of equipment downtime per year — more than 15 hours per week.
With smart IoT predictive maintenance solutions, industrial companies can detect machine defects in an early stage: before an actual breakdown. This gives them the optimal response time to schedule asset maintenance and prevent unplanned downtime.
E.E: What are the most innovative products marketed?
G.M:
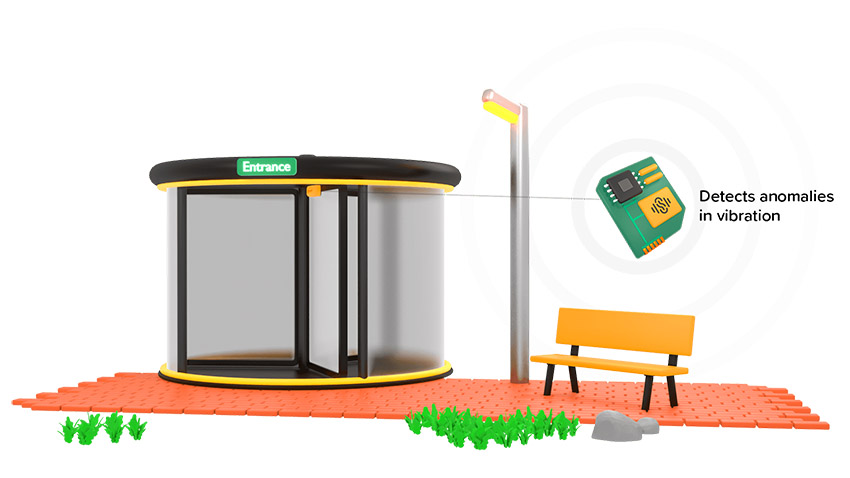
Vibration sensor to monitor the performance of automatic doors
To ensure the automated sliding doors reach an operational time of over 98%, the movement of the doors is monitored with vibration sensors. Sensor information is sent to the cloud via a LTE-M Gateway, and in the cloud an algorithm calculates the moment the door will possibly fail. Our customer is now able to schedule maintenance well in advance and prevent unplanned downtime. This helps to guarantee a safe and continuous people flow.
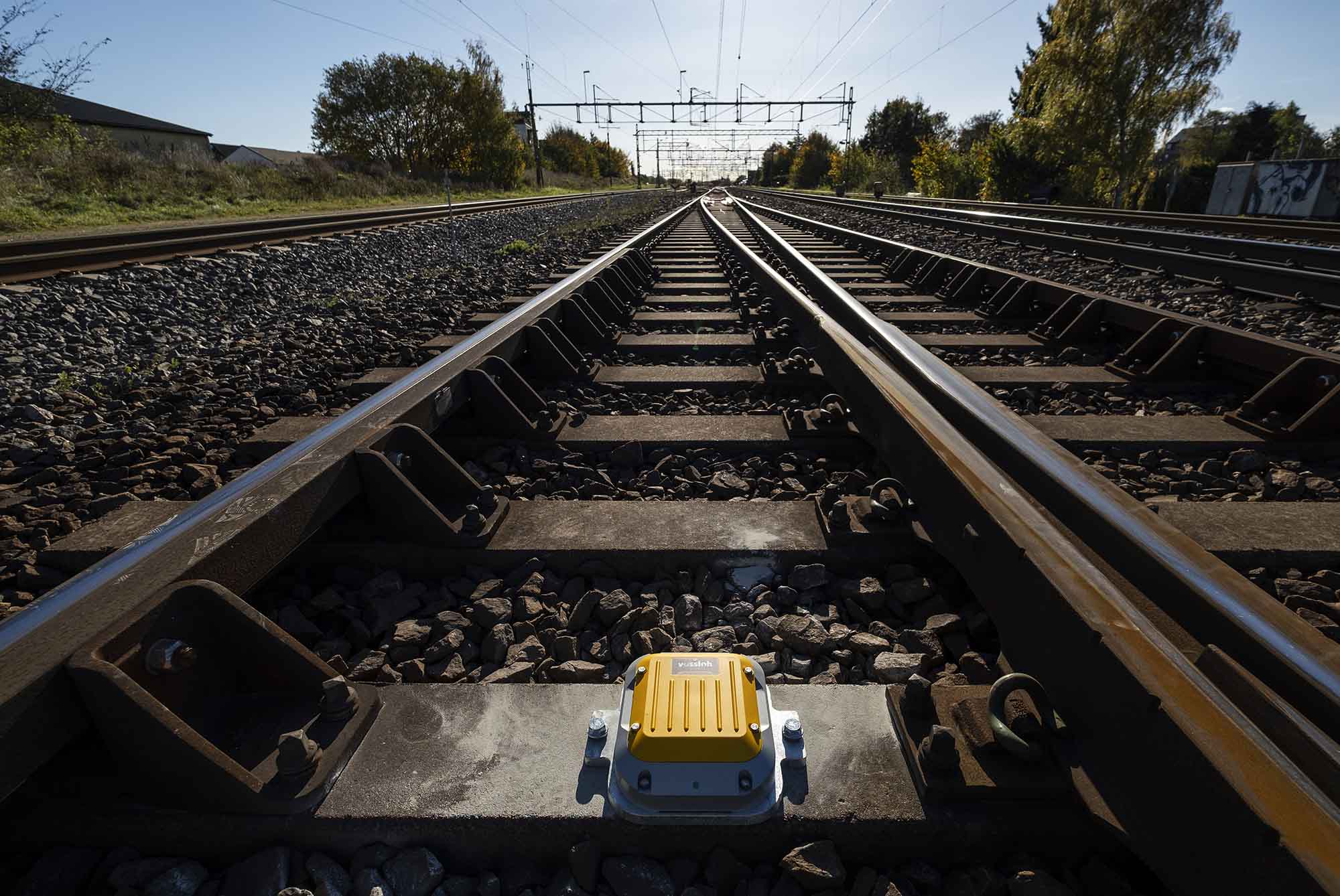
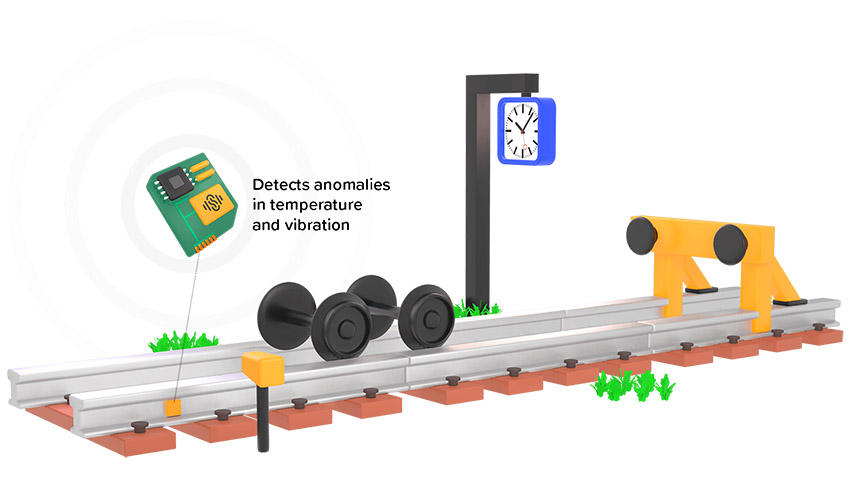
Vibration sensor to monitor the displacement of railway tracks
Sensorfy developed a smart sensor which is placed at the railway track. Through vibration monitoring we measure the displacement of the rails so we can predict when maintenance of the track is needed.
Electronic egg to reduce the number of broken eggs by monitoring the calibration of conveyor belts
Sensorfy developed an electronic egg that contains several motion and vibration sensors. These sensors register all movements of a regular egg during its journey on the conveyer belt. The data extracted from this proces creates a clear image of the weak spots on the conveyer belt. This enables Vencomatic Group to take exactly the right measures to smoothen the travel of fresh eggs.
Real-time access control mechanism for containers
In close cooperation with DBI, Sensorfy developed a real-time access control mechanism for containers. The control system is connected to the cloud 24/7 and supports city halls in the waste management process. Containers can be remotely controlled and monitored making sure that containers are always working and emptying routes are optimized.
E.E: What estimations do you have for 2022/2023?
G.M: Our expectations for end of 2022 and 2023 are that predictive maintenance will continue to grow and more and more companies are ready to start implementing smart IIoT solutions that enable predictive maintenance.
With the current global situation, the trend of a more sustainable industrial industry will also play an important role in pushing the adoption of IIoT solutions that enable predictive maintenance. Our focus for the coming period is to continue helping OEMs in their transition towards servitization with IoT solutions that enable predictive maintenance. We are ready to help innovate their business models and make their industrial assets smart.

